Go-To Financial Metric Primer: EBIT, EBITDA, and EBITA Definitions and NetSuite Report Tutorial
Financial metrics help measure your company's performance so you can make better decisions. Therefore, you need a way to generate fast, reliable financial reports.
We understand how important quick, transparent reporting is to your company. You must be able to measure and report on its profitably accurately, or you can’t satisfy investors and make wise decisions. You need an easy process for collecting and organizing data, particularly for EBIT, EBITA, and EBITDA metrics.
Our guide covers the meaning of EBITA, EBITDA, and EBIT, how to use them, and how to create reports for them in NetSuite.
SuiteDynamics partners with NetSuite to customize and implement NetSuite Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and other products. Our company also employs financial experts who can help build the most efficient and effective custom reports possible, so your business has the data it needs to compete.
Schedule a free consultation and start collecting and organizing data that helps your business own the marketplace.

What Does EBITA Mean?
EBITA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, and Amortization. It's a financial metric used to evaluate a company's operating performance without the effects of monetary and accounting decisions and tax environments. Here's a breakdown of its components.
Earnings: Profit a company generates from its operations.
Before: Earnings calculated before deducting the specified expenses.
Interest: Costs incurred from borrowing money. Expenses are excluded in the EBITA calculation to assess the company's operational profitability regardless of its financing structure.
Taxes: Vary significantly depending on the company's location and legal structure. Excluding taxes allows for a better comparison of operational efficiency across different entities and jurisdictions.
Amortization: Gradual write-off of the intangible assets' value over time.
Investors and analysts use EBITA when focusing on a company's core operational profitability. According to the Corporate Finance Institute (CFI), net income indicates a company’s overall profitability, but EBITA reflects general proceeds.
“The true performance of a company’s operations can be determined when the effects associated with taxes, interest, and amortization are removed,” CFI explains. “Since the effect of such items is excluded in EBITA, investors consider it an important measure to determine a company’s true earnings.”
Why It's Used
EBITA is useful for analyzing companies with significant intangible assets. By excluding amortization, EBITA can offer a clearer view of the operating performance of such businesses.
However, some prefer EBITDA as a more comprehensive operational performance view because it excludes depreciation.
SuiteDynamics financial experts can help customize financial processes and reporting software that helps collect and organize data in ways that benefit your company most. Tell us what you need and watch your efficiency skyrocket.

What Does EBITDA Mean?
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It measures a company's operating performance by calculating its earnings before subtracting interest expenses, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
The concept, of course, is very similar to EBITA but adds “depreciation” to the list of exclusions.
Depreciation is the systematic allocation of a tangible asset’s cost over its useful life. It represents the decreased value of physical assets (like machinery, buildings, and vehicles) used in a business over time.
Removing the impact of non-cash expenses (depreciation and amortization), as well as interest and taxes, helps EBITDA provide a clearer view of operational profitability and cash flow potential. It can more easily compare the performance of companies across different industries or with varying capital structures.
“[EBITDA] can give an analyst a quick estimate of the value of the company, as well as a valuation range, by multiplying it by a valuation multiple obtained from equity research reports, publicly traded peers, and industry transactions, or M&A,” CFI explains.
Investors and analysts often use EBITDA as a proxy for a company's cash flow from operations. Yet, EBITDA doesn’t account for capital expenditures or changes in working capital, which help you understand the actual cash flow available to fund operations, debt obligations, and investments.
Why It's Used
EBITDA eliminates the effects of non-operational factors to offer a cleaner profitability comparison between companies and industries. It's beneficial in sectors with significant investments in physical and intangible assets.
Schedule a free consultation with SuiteDynamics to discuss all your reporting needs. Our financial experts can ensure your company has the right processes for easy and accurate data collection that equips it to succeed.

What Does EBIT Mean?
Sometimes, companies opt for the simpler EBIT or Earnings Before Interest and Taxes. This metric calculates a company's operating income by excluding only interest expenses and taxes from its net income. EBIT provides insight into the profitability of a company's core operations without considering the impact of its financial structure (debt vs. equity financing) and tax obligations.
EBIT is particularly useful for analysts and investors who want to understand a company's ability to generate profits from its core business activities. EBIT is like operating income, though operating income can have minor differences in how companies calculate it based on their accounting practices. For instance, they may change how they classify operating vs. non-operating items.
Why It's Used
EBIT offers a straightforward view of a company's operating performance by removing the effects of its financing structure and tax obligations. Since it includes depreciation and amortization, it reflects the costs associated with tangible and intangible assets. It also offers a more conservative measure of operational profitability.
SuiteDynamics experts can design reporting solutions that provide your company with any financial metrics it needs to succeed. Schedule a free consultation and see how easy reporting can become.
Key Differences
Usefulness
Each metric serves a different purpose based on the appropriate factors for the business under evaluation. EBITDA compares companies across industries by normalizing differences in financing and capital expenditures. EBITA is particularly relevant for companies with significant intangible assets. EBIT, being the most conservative, is useful for assessing operational performance, including the cost of tangible and intangible assets.
Industry Application
The preference for one metric over another can vary by industry, depending on the nature of the capital investments (tangible vs. intangible assets) and how they impact operational performance analysis.
Important Note:
Neither EBIT, EBITA, or EBITDA are financial metrics approved by the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Consequently, you must also use other measures if your company complies with those standards.
Creating EBIT, EBITA, and EBITDA Reports in NetSuite
NetSuite doesn’t come with EBIT, EBITA, or EBITDA reports out of the box. Fortunately, you can build one quickly in a few steps.
The process remains generally the same for all report types. Simply adjust the financial section list based on the kind of report you need (Step #6).
- Open the native NetSuite Income Statement.
- Click Customize.
- Click Add Header and Summary Rows.
- Title the Header and Summary labels either “EBITDA,” “EBITA,” or “EBIT”—whichever report you want to create.
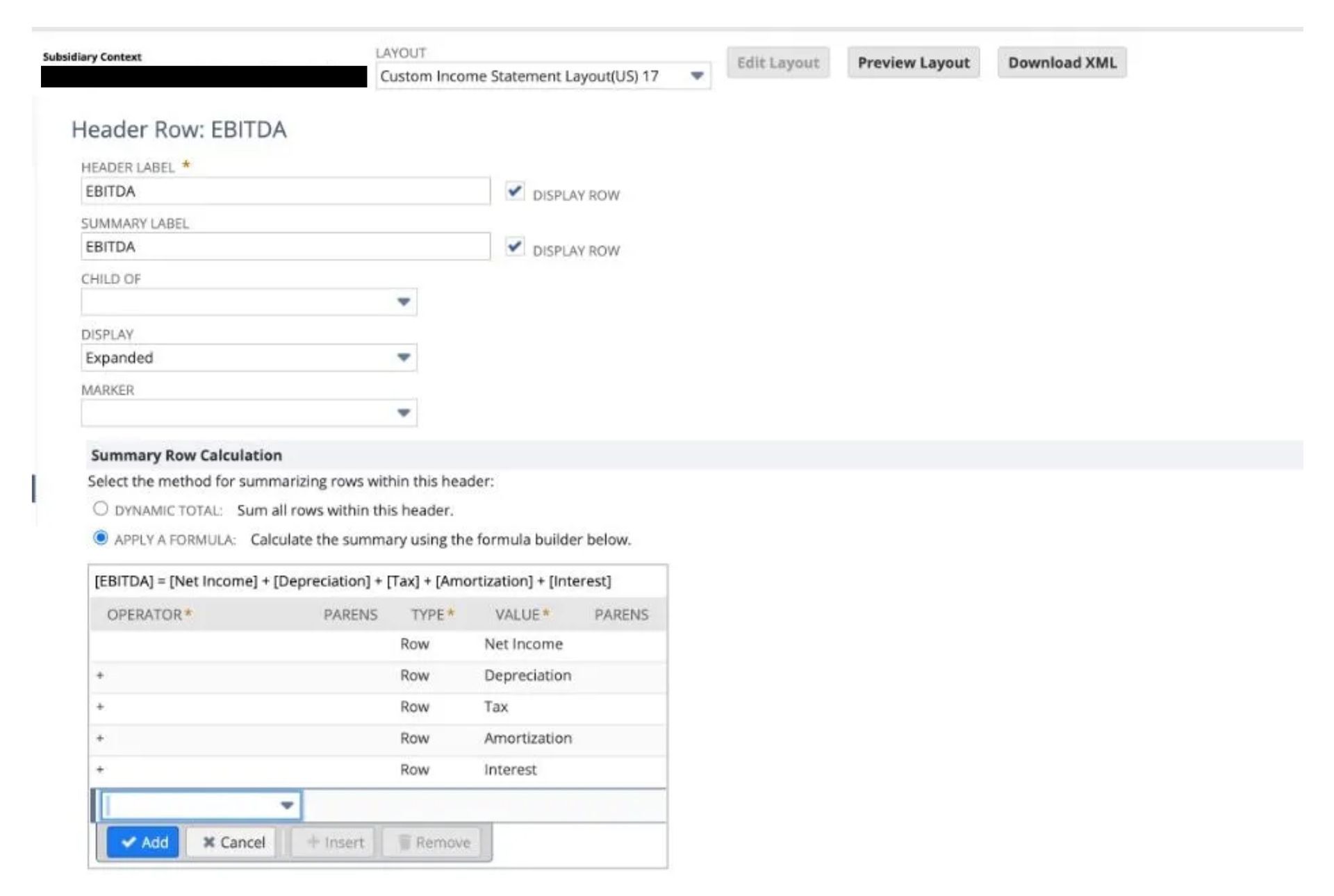
5. Click Add Financial Section.
a. Create a New Section.
6. Create one financial section for each type of account you add back. (Of course, c and d are optional.)
a. Interest
b. Tax
c. Deprecation
d. Amortization
7. Enter the section name in the Header label and click the Display row.
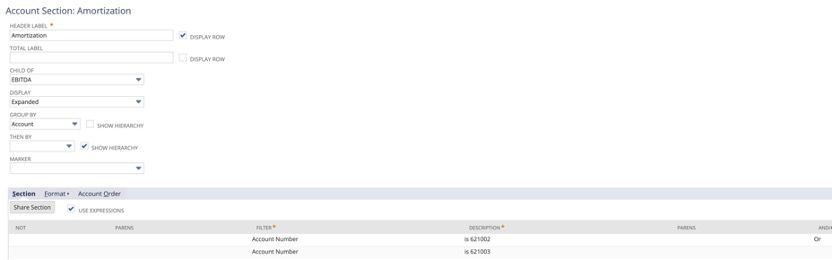
8. Select your Header from the Child Of dropdown.
9. Uncheck Show Hierarchy for Group by Account.
10. Check the Use Expression box under the section header.
11. Use the Or function to add every account number you want to include in this section.
12. Under the Format Section, check the Reverse Sign box.
a. Natively, NetSuite brings the expense accounts over as a negative. This process will reverse that action.
13. After all sections have been created, go back to the EBITA, EBITDA, or EBIT summary.
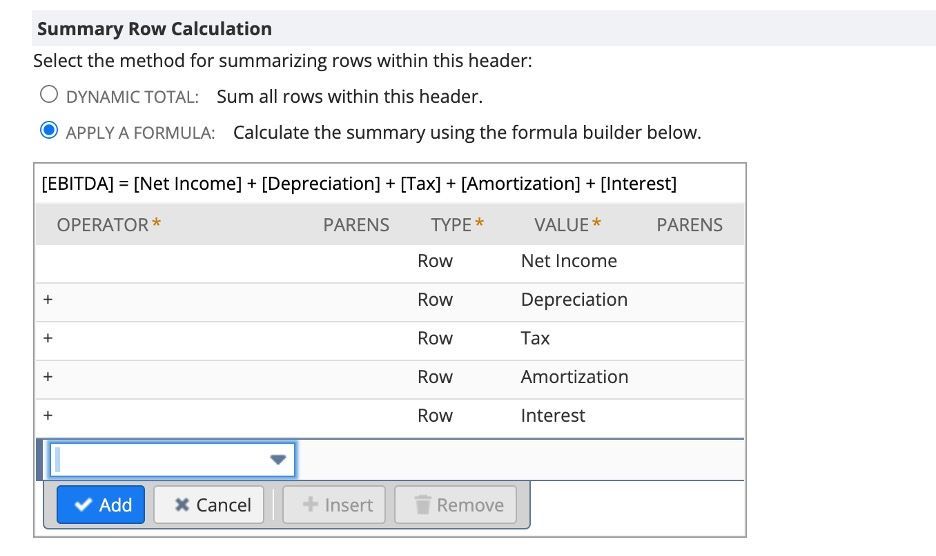
14. Click Apply a Formula Radio.
15. Select Type “Row” and Value Net Income.
16. Use the “+” operator to add each financial section to the formula.
17. Save your report with the desired name.
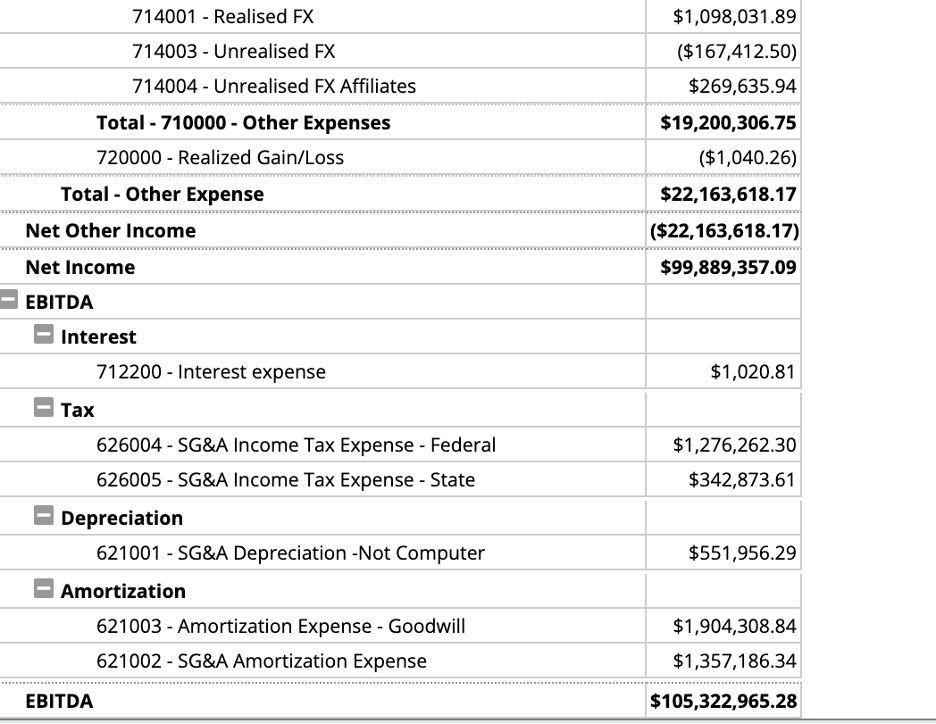
18. Your income statement will then feature an additional EBITA, EBITDA, or EBIT section.
If you have other reporting needs, schedule a consultation with SuiteDynamics. You’ll get quality customization built by people who understand both software and finance.
Get Custom Reports That Actually Work
Some NetSuite reports are difficult to customize unless you have experience with the system. You can easily waste time building one that doesn’t work well and causes more problems than it solves.
We know you don’t have the spare time or staff to invest in terrible reporting. SuiteDynamics employs NetSuite and financial experts to create effective custom reports that organize data into easily accessible and digestible documents.
Tell us about your reporting needs, and we’ll ensure you get the software necessary to meet them and satisfy stakeholders.
We pull information from NetSuite material, SuiteDynamics experts, and other reliable sources to compose our blog posts and educational pieces. We ensure they are as accurate as possible at the time of writing. However, software evolves quickly, and although we work to maintain these posts, some details may fall out of date. Contact SuiteDynamics experts for the latest information on NetSuite ERP systems.
Part of this text was generated using GPT-3, OpenAI’s large-scale language-generation model. After generating the draft language, our team edited, revised, and fact-checked it to ensure readability and accuracy. SuiteDynamics is ultimately responsible for the content of this blog post.











